Head & Neck Cancer
Home » Specialties » Head & Neck Cancer
Head and Neck Cancers
Head and neck region can be divided into many subsites and cancers arise from all of them.
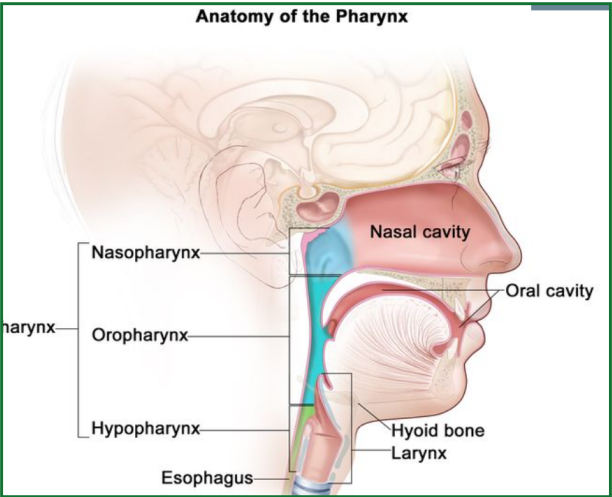
Commonly the region can be divided into:
1. Lips
2. Oral cavity including gums, buccal mucosa & oral tongue
3. Palate- Hard & soft
4. Oropharynx-Base of tongue & tonsils
5. Nasopharynx
6. Larynx or the breathing pipe which includes vocal cords
7. Hypopharynx or the region behind the larynx. It continues as Oesophagus or the food
pipe.
Signs and symptoms of oral cancer
1. A sore on the lip or in the mouth that does not heal.
2. A lump or thickening on the lips or gums or in the mouth.
3. A white or red patch on the gums, tongue, or lining of the mouth.
4. Bleeding, pain, or numbness in the lip or mouth.
5. Loose teeth or dentures that no longer fit well.
6. Trouble chewing or swallowing or moving the tongue or jaw.
7. Swelling of jaw.
8. Sore throat or feeling that something is caught in the throat.
9. Change in voice.
10. Nasopharyngeal cancers: A lump in the nose or neck;Trouble breathing or
speaking; Nosebleeds; Trouble hearing; Pain or ringing in the ear; Headaches.
Risk Factors for Head and Neck Cancers:
1. Tobacco Consumption: It is considered as the single largest cause of all head and neck cancers worldwide. This includes both smoking and smokeless forms. Around 80-90% of head and neck cancers can be attributed to use of tobacco.
2. Alcohol Consumption: Is also associated with increased risk of cancers.
3. Viruses: Certain viruses are associated with cancers. Epstein Barr virus is linked to nasopharyngeal cancers. Human Papilloma Virus is associated with oropharyngeal cancer.
4. Trauma: Sustained trauma like sharp tooth or history of dental surgery is sometimes seen in patients with oral cancers.
Diagnosing an oral cancer
1. Physical exam of the lips and oral cavity: An exam to check the lips and oral
cavity for abnormal areas. The doctor will feel the entire inside of the mouth & the neck will be felt for swollen lymph nodes.
2. Endoscopy: An endoscope is inserted through the mouth and pharynx to look for
abnormal areas and to take a biopsy.
3. Biopsy: The removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist.
4. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or CT scan : will be taken of the head and
neck region to assess the extent and spread of the disease in the local area and the neck nodes.
5. PET Scan: It is a whole body scan utilising a special dye like FDG that assesses the spread of disease throughout the body.
Treatment of Head and neck cancers
There are 3 main modalities by which treatment is undertaken.
1. Surgery: Surgery is undertaken mainly for oral cavity cancers. This includes wide local excision of the tumor with neck dissection followed by reconstruction of the area by a plastic surgeon.
2. Radiation Therapy: In cancers of oropharynx, larynx, nasopharynx and hypopharynx
radiation therapy is preferred modality of treatment along with concurrent chemotherapy. Radiotherapy is given daily over a period of 6-7 weeks depending upon the stage of the cancer. It can be given after surgery also in oral cavity or larynx cancers to reduce the chances of recurrence depending upon the risk factors in histopathological report.
3. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs either via the bloodstream or orally to kill the cancer cells. It can be given before the surgery in large cancers to reduce their size or along with radiotherapy to cure the cancer. Chemotherapy alone is used in metastatic cancers.