Cervix Cancer
Home » Specialties » Uterix & Cervix Cancer
Treatment Options
In most nonpregnant women, the uterus is about 3 inches long. The lower, narrow end of the uterus is the cervix, which leads to the vagina.
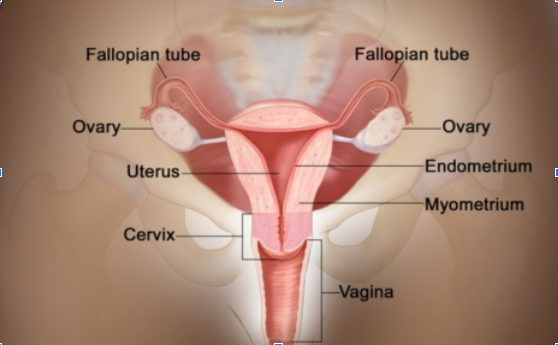
Cancer can develop either inside the uterus which is called endometrial cancer or in the cervix which is called cervix cancer.
Risk Factors:
A. Endometrial Ca:
1-Taking estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy (HRT) after menopause.
2-Taking tamoxifen to prevent or treat breast cancer.
3-Obesity.
4-Type 2 diabetes.
5-A family history of endometrial cancer in a first-degree relative (mother, sister, or daughter).
6-Having certain genetic conditions, such as Lynch syndrome.
B. Cervical Cancer:
1-Long-lasting (persistent) infection with high-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV) causes virtually all cervical cancers.
2-Socioeconomic Factors which include people from lower strata have been found to be more susceptible.
3-Early initiation of sexual activity and bearing more children
4-Weakened immune system due to disease like HIV or immunosuppressants have been 5-found to accelerate the disease process.
5-Smoking.
Signs and Symptoms:
1. Vaginal bleeding or discharge not related to menstruation (periods).
2. Vaginal bleeding after menopause.
3. Difficult or painful urination.
4. Pain during sexual intercourse.
5. Pain in the pelvic area.
Screening and Prevention of Cervical Cancer:
1. Screening: 2 tests Pap Smear and HPV genetic testing can identify people having early stages of cancer. These screening tests are recommended for females from 30-65 years of age.
2. HPV vaccination: HPV vaccination is a safe and effective way to help prevent cervical cancer.The HPV vaccine offers the most protection when given before a person becomes sexually active. It is recommended for boys and girls between the ages of 9-25. HPV infection can also lead to other cancers in the genital the region, anal canal cancer & oropharyngeal cancers the vaccine is very useful in preventing a wide variety of cancers.
Treatment:
1. Surgery: Surgery is the standard of care in endometrial cancers and early stage cervical cancers.
2. Radiation Therapy: Is required in endometrial cancers in late stage I & Stages II & III after surgery. In Cervical cancers all stages can be treated along with concurrent chemotherapy and can completely cure the cancer.
The 2 types of radiation therapy that are utilised are:
a. External Beam Radiotherapy– uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the area of the body with cancer.
b. Internal Radiation therapy/ Brachytherapy: Uses radiation sources kept in proximity to the tumor to deliver high doses of radiation to kill tumor cells. It is a surgical procedure and is performed under anesthesia.
3. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy (also called chemo) uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing.